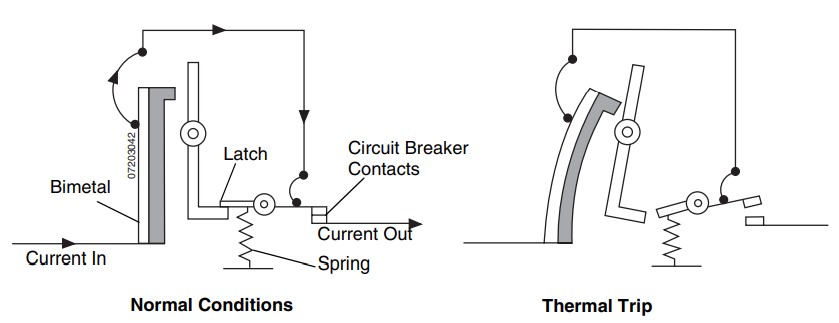
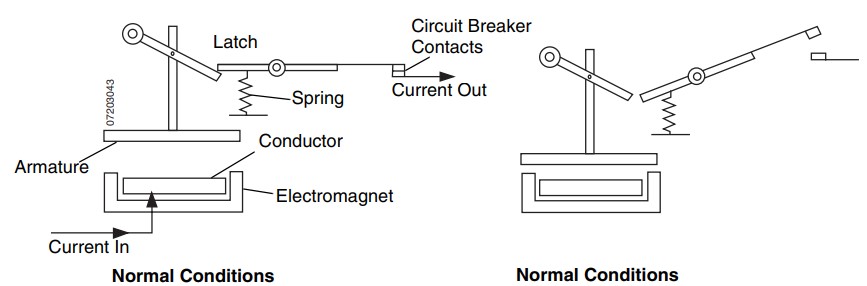
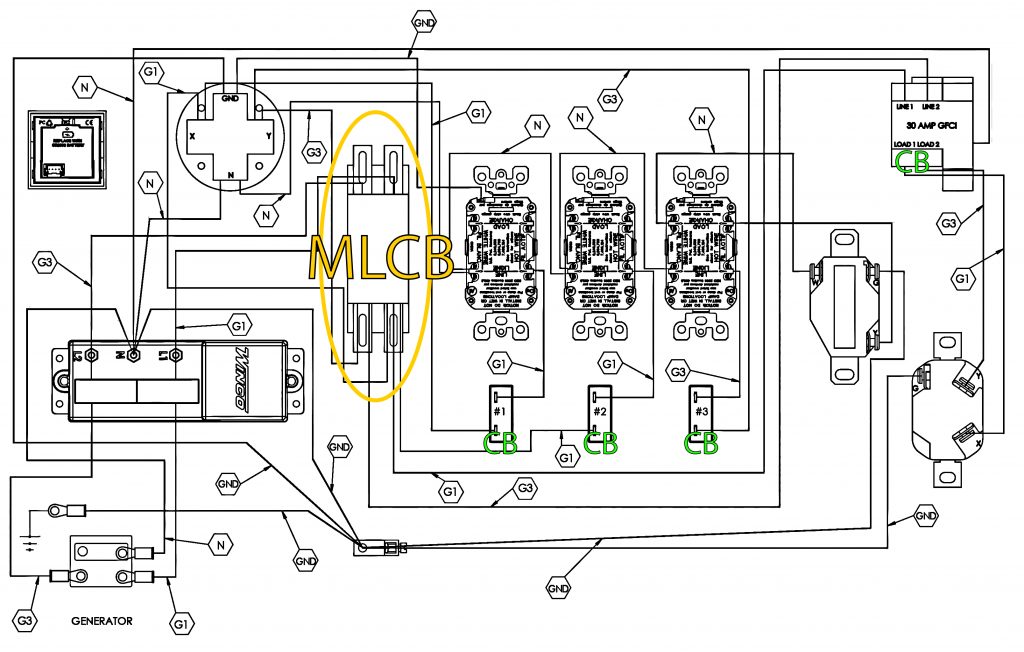
Safety is important and the main line circuit breaker (MLCB) plays a key role in protecting people and equipment. This main breaker is placed between the generator end and the load. All of the electrical current goes through this breaker. If there is too much load it will trip and interrupt the current to help and prevent damage or overload.
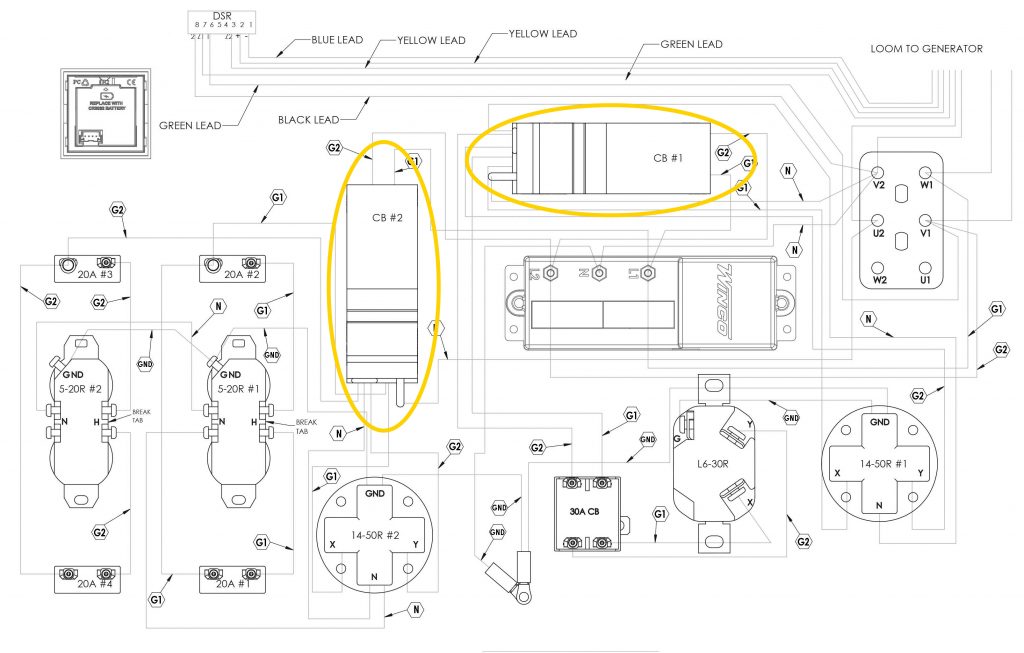
Many of our products have multiple receptacles. The MLCB serves as the main safety gate and feeds additional circuit breakers that protect the individual receptacles. The picture below shows a WL18000VE and how the smaller circuit breakers (CB) and receptacles all wire through the MLCB. The MLCB is normally rated at 100-125% of the generator output.
In some applications it makes sense to have dual breaker systems. For example, the WL22000VE panel below has two breakers that provide the main line protection for half of the receptacle panel. The ratings of both breakers are specified to be equal to 100-125% of the total generator output.